Introduction — A Practical Hook for New Developers
If you’re starting web development in 2025, learning javascript node js is one of the fastest ways to build real, useful projects. Imagine shipping a chat app, API, or automation tool using the same language on both client and server — that’s the practical power Node.js gives you. This guide explains the essentials clearly, includes hands-on steps, and points out the pitfalls beginners usually hit so you can skip the headaches and start building.
What Is JavaScript vs. What Is Node.js? (Short Comparison)
Before we code, let’s clear terminology:
- JavaScript is the programming language used for web browsers and many other environments, from servers and databases to mobile and desktop applications.
- Node.js is a runtime that executes JavaScript on the server (outside the browser) using Google’s V8 engine.
Why that matters: using Node.js means you can run the same syntax on the server, access files, databases, and network resources, and use a massive package ecosystem (npm) to speed development.
Why Learn JavaScript Node.js in 2025? (Key Reasons)
- Unified stack: front-end and back-end in one language reduces context switching.
- Fast I/O: Node’s event-driven, non-blocking model is ideal for real-time apps.
- Its vast ecosystem is powered by npm, which provides reusable packages for nearly any requirement.
- Serverless friendly: Node.js is widely supported on platforms like Vercel, Netlify, and AWS Lambda.
- Job demand: Full-stack and backend roles still list Node.js as a top skill.
If you’re a student or a developer starting out, Node.js offers the quickest path to deployable projects.
Quick Setup: Install Node.js & Verify (Hands-on steps)
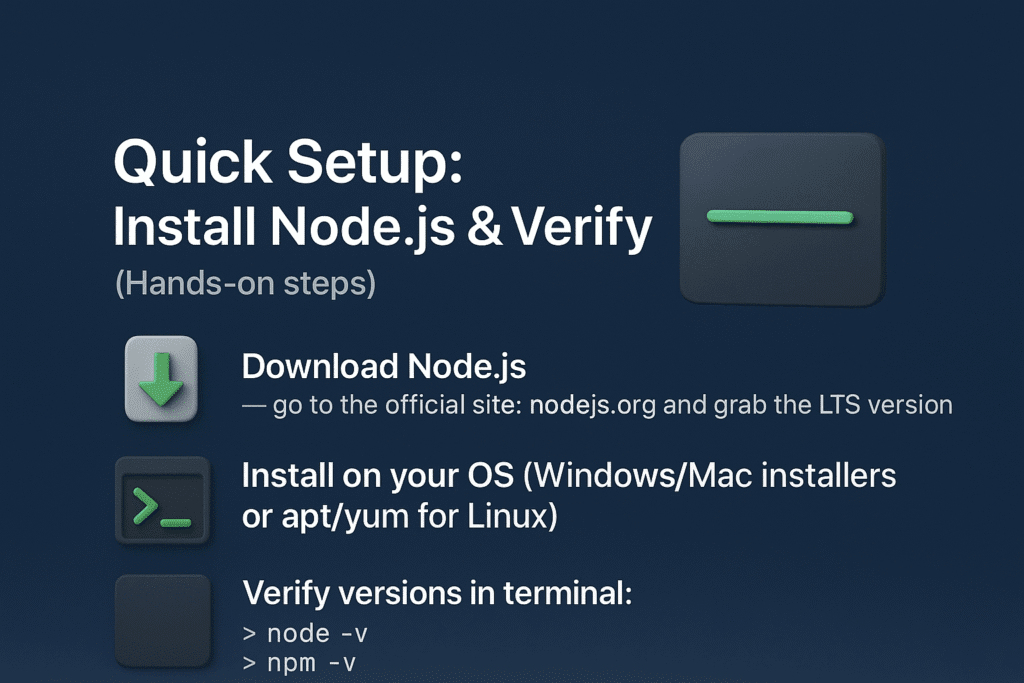
- Download Node.js — go to the official site: nodejs.org and grab the LTS version.
- Install on your OS (Windows/Mac installers or
apt/yumfor Linux). - Verify versions in terminal:
node -v
npm -v
- Create a folder, add
hello.js, paste:
console.log("Hello, Node.js!");
- Run:
node hello.js
ok now If you see the message, you’re ready to move forward.
First Real Example: A Tiny HTTP Server
This short script shows Node.js as a web server:
const http = require('http');
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/plain'});
res.end('Hello from Node.js!');
});
server.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server running at http://localhost:3000/');
});
Open http://localhost:3000 to confirm. This minimal example illustrates core Node.js concepts: modules (http), callbacks, and listening for connections.
Core Concepts (Simple, Practical Explanations)
Modules
Node.js uses modular code. Built-in modules include fs, path, and http. Third-party modules are installed via npm:
npm init -y
npm install express
Asynchronous / Event-driven
Node’s non-blocking model means I/O operations (disk, network) don’t freeze your app. Use callbacks, promises, or async/await to manage flow.
npm
npm is the package manager with millions of modules. Learn to read package READMEs, check maintenance activity, and avoid untrusted packages.
JavaScript (Browser) vs Node.js vs Deno — Quick Table
| Feature | Browser JavaScript | Node.js | Deno |
|---|---|---|---|
| Runs in | Browser | Server / CLI | Server / CLI |
| Package manager | n/a (bundlers) | npm | Built-in (URL imports) |
| Security model | Sandbox | File & network access by default | Secure by default (explicit permissions) |
| Use case | UI, DOM | APIs, servers, scripts | Modern runtime, secure scripts |
Takeaway: Deno is interesting, but Node.js remains the production standard with the larger ecosystem in 2025.
Common Beginner Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
- Blocking the event loop (e.g., heavy synchronous tasks).
Fix: use async APIs, worker threads, or microservices. - Poor error handling — uncaught exceptions crash servers.
Fix: handle promise rejections, usetry/catch, and centralized error middleware (Express). - Ignoring dependency hygiene (outdated or untrusted packages).
Fix: check package activity, usenpm audit, and pin versions. - Not reading logs — errors often reveal the fix.
Fix: enable logs and learn to read stack traces.
Best Libraries & Starter Tools (Practical Picks)
- Express — minimal and flexible web framework for APIs.
- Fastify — high-performance alternative to Express.
- Mongoose — MongoDB ODM for structured schemas.
- dotenv — load environment variables securely.
- nodemon — auto-restart server during development.
Install with npm install express dotenv and follow examples in each package’s documentation.
A Short Project Roadmap (From Zero to Deployable)
- Week 1: learn Node basics, console scripts,
fs, and modules. - Week 2: build a simple Express API with routes and JSON responses.
- Week 3: connect a database (MongoDB or SQLite) and add CRUD operations.
- Week 4: deploy to a serverless platform like Vercel or a basic VPS.
Structure each project with clear folders: routes/, controllers/, models/, and config/.
Fresh Perspectives for 2025 (What New Beginners Should Know)
- Serverless workflows make deployment trivial — developers use Node.js functions on demand.
- Edge computing services like Cloudflare Workers and Vercel Edge Functions blur the traditional separation between server and CDN, enabling Node.js patterns to run at the edge—though developers must still account for cold starts and global latency.
- AI integrations: Node.js frequently orchestrates API calls to AI services — learn async patterns and rate-limit handling.
- Security by default: validate inputs, sanitize outputs, and adopt security headers (Helmet for Express).
Visuals & Learning Aids (How to Use Them)
- Infographic idea: “Node.js Flow — Request → Event Loop → Async I/O → Response” (use on tutorial pages).
- Table: we used a comparison table above to clarify choices.
- Suggested images: project folder structure, simple sequence diagrams of event loop, and screenshots of terminal commands.
(When publishing on your site, include images with descriptive alt text like: “Node.js server setup command output”.)
Where to Read Next (Helpful Links)
- Official Node.js docs: nodejs.org — the canonical reference.
- npm registry: npmjs.com — explore packages.
- MDN Web Docs: covers JavaScript fundamentals and related web APIs.
Also link internally to your site’s deeper tutorials like /coding-tutorials/ or /tech-guides/ to keep readers exploring.
Conclusion & Next Steps (Clear CTA)
Mastering javascript node js basics unlocks faster prototyping and real deployment skills. Start small: install Node, run the “hello” script, then build an Express API. Practice is the accelerator.
Call to action: Try the small project roadmap above this week. Share your first Node.js server in the comments below, subscribe for more step-by-step guides, and check out our related tutorials on building APIs and deploying to serverless platforms.



